Understanding Market Research
Market research is a cornerstone of effective marketing. It involves systematically gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a market, including insights into the target audience, competitors, and overall industry trends. This research is crucial for making informed decisions and developing strategies that resonate with consumers.
Types of Market Research: Primary and Secondary

1 Primary Research
Description: Primary research involves collecting firsthand data directly from sources. This data is original and tailored to address specific research questions.
Methods:
Surveys: Structured questionnaires designed to gather quantitative data from a large audience. Surveys can be conducted online, via phone, or in person.
Example: A new coffee shop conducts online surveys asking local residents about their coffee preferences, ideal cafe ambiance, and expected price range.
Interviews: In-depth, qualitative data collection through one-on-one conversations. Interviews provide detailed insights into individual opinions and experiences.
Example: A fashion brand conducts interviews with a select group of customers to understand their preferences for sustainable clothing materials.
Focus Groups: Guided group discussions aimed at collecting diverse perspectives on a specific topic. Focus groups help identify common themes and unique insights.
Example: A tech company organizes focus groups to gather feedback on a prototype of a new smartphone, discussing features, design, and usability.
Observations: Monitoring consumer behavior in real-life settings to gain insights into their actions and preferences without direct interaction.
Example: A retail store observes customers’ in-store behavior, noting which sections attract the most attention and how they navigate the space.
2 Secondary Research
Description: Secondary research involves analyzing existing data that was collected for other purposes. This data is often readily available and cost-effective to obtain.
Sources:
Reports: Industry reports, market analysis reports, and research studies provide valuable insights into market trends and consumer behavior.
Example: A startup analyzes an industry report on e-commerce trends to identify opportunities for launching a new online platform.
Publications: Academic journals, trade publications, and business magazines offer research findings and expert opinions.
Example: A pharmaceutical company reviews academic journals to stay updated on the latest developments in drug research and innovation.
Online Sources: Websites of market research firms, government databases, and online repositories provide access to a wealth of information.
Example: A real estate firm uses government databases to analyze demographic data and economic indicators for potential investment locations.
Research Methodologies and Tools
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research involves collecting numerical data that can be quantified and analyzed statistically. It is used to identify patterns, measure variables, and predict outcomes.
Tools:
SPSS and SAS: Software for advanced statistical analysis, used to process and analyze large datasets.
Example: A marketing agency uses SPSS to analyze survey data, identifying correlations between consumer demographics and purchasing behaviors.
Google Analytics: A web analytics tool that tracks and reports website traffic, providing insights into user behavior and engagement.
Example: An e-commerce site uses Google Analytics to monitor visitor behavior, track conversions, and optimize their online marketing campaigns.
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research focuses on understanding the underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations behind consumer behavior. It provides depth and context to quantitative findings.
Tools:
NVivo and Atlas.ti: Software for qualitative data analysis, used to code and analyze textual data from interviews, focus groups, and open-ended survey responses.
Example: A healthcare provider uses NVivo to analyze patient feedback from focus groups, identifying key themes related to service satisfaction.
SurveyMonkey and Qualtrics: Online survey tools that facilitate the creation, distribution, and analysis of surveys.
Example: A non-profit organization uses SurveyMonkey to collect feedback from donors and volunteers, helping to improve engagement strategies.
Consumer Behavior

Understanding consumer behavior is essential for developing effective marketing strategies. Consumer behavior refers to the actions and decision-making processes of individuals as they select, purchase, use, and dispose of products and services.
Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Cultural Factors
Culture, subculture, and social class significantly influence buying behavior. These factors shape individuals’ values, perceptions, and preferences.
Example: In many Asian cultures, collectivism drives purchasing decisions, leading to a preference for products that emphasize family values and community well-being. For instance, a marketing campaign for a family-oriented product in India might highlight the product’s benefits for the entire household, aligning with cultural values.
Social Factors
Family, roles, and status within social groups impact consumer behavior. These factors determine how individuals perceive themselves and their purchasing choices.
Example: A teenager may prefer certain brands of clothing influenced by peer groups and social media trends. A fashion brand targeting teenagers might collaborate with popular social media influencers to promote their products, leveraging the influence of peer recommendations.
Personal Factors
Age, occupation, lifestyle, and economic situation shape buying patterns. These factors are unique to each individual and can vary widely.
Example: Young professionals might invest in premium tech gadgets that complement their fast-paced lifestyle. A tech company targeting this demographic could emphasize features like productivity apps, sleek design, and portability in their marketing campaigns.
Psychological Factors
Motivation, perception, learning, beliefs, and attitudes drive consumer actions. These factors influence how individuals interpret and respond to marketing messages.
Example: A consumer motivated by health consciousness may choose organic food products over conventional ones. A food brand promoting organic products might focus on health benefits, natural ingredients, and eco-friendly packaging to appeal to health-conscious consumers.
Consumer Decision-Making Process
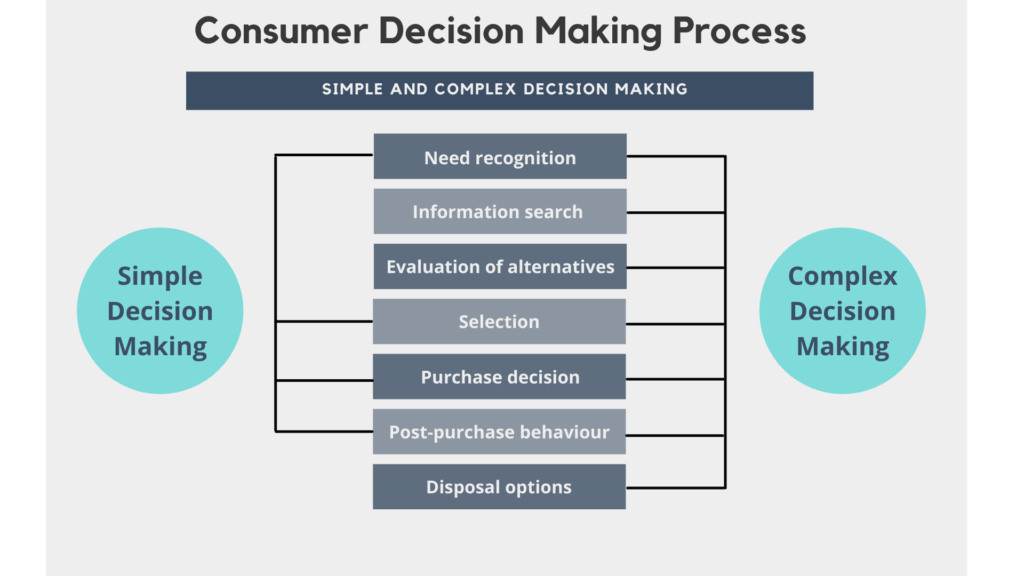
Problem Recognition
The consumer identifies a need or problem that requires a solution.
Example: A person realizes they need a new phone as their old one starts malfunctioning. This recognition triggers the search for a suitable replacement.
Information Search
The consumer seeks information about how to fulfill this need, exploring various options and gathering data.
Example: Researching online reviews, asking friends for recommendations, and visiting stores to compare different smartphone models and features.
Evaluation of Alternatives
The consumer compares different products and brands, weighing the pros and cons of each option.
Example: Comparing features, prices, and brand reputation of several smartphones. A consumer might create a shortlist of potential models based on criteria like camera quality, battery life, and user reviews.
Purchase Decision
The consumer decides on the product and makes the purchase, influenced by their evaluation and external factors like promotions or availability.
Example: Choosing to buy a specific smartphone model from an online retailer offering a discount and free shipping.
Post-Purchase Behavior
The consumer evaluates their satisfaction with the purchase, which can influence future buying decisions and brand loyalty.
Example: Sharing reviews online, recommending the phone to friends if satisfied, or expressing dissatisfaction through social media if the product does not meet expectations.
Data Analysis and Interpretation

Data analysis is the process of examining, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data to discover useful information, draw conclusions, and support decision-making. Effective data analysis is crucial for developing successful marketing strategies.
Analyzing Market Data

Descriptive Analysis
Descriptive analysis summarizes data to describe what has happened. It provides a clear picture of historical trends and patterns.
Tools:
Charts and Graphs: Visual representations of data that highlight key trends and patterns.
Example: Analyzing monthly sales data using bar charts to identify peak sales periods and seasonal trends.
Summary Statistics: Measures such as mean, median, and mode that provide a concise summary of data distribution.
Example: Calculating the average customer satisfaction score from survey responses to gauge overall sentiment.
Inferential Analysis
Inferential analysis makes predictions or inferences about a population based on a sample. It helps identify relationships and test hypotheses.
Tools:
Regression Analysis: A statistical method used to examine the relationship between variables and predict outcomes.
Example: Using regression analysis to predict future sales based on past performance and market conditions.
Hypothesis Testing: A method of making decisions or inferences about population parameters based on sample data.
Example: Testing whether a new marketing campaign has significantly increased brand awareness compared to previous efforts.
Prescriptive Analysis
Prescriptive analysis provides recommendations for actions based on data analysis. It helps determine the best course of action to achieve desired outcomes.
Tools:
Optimization Algorithms: Mathematical models that identify the best solutions from a set of feasible options.
Example: Using optimization algorithms to determine the most efficient allocation of marketing budget across different channels.
Simulation Models: Computational models that simulate various scenarios to predict the impact of different strategies.
Example: Running simulations to assess the potential effects of a price change on sales and profitability.
Using Insights to Inform Marketing Strategies
Segmentation
Segmentation involves dividing the market into distinct groups of consumers with similar needs or characteristics. It allows for more targeted and effective marketing efforts.
Example: Segmenting a market based on demographics, such as age or income level, to tailor marketing efforts. A beauty brand might create different campaigns for teenagers, young adults, and older consumers, addressing the unique needs and preferences of each group.
Targeting
Targeting involves selecting specific segments to focus marketing efforts on. It ensures that resources are directed towards the most promising opportunities.
Example: A luxury brand targeting high-income consumers with premium products. The brand might use exclusive events, personalized services, and high-end advertising channels to reach their target audience.
Positioning
Positioning involves creating a unique image and identity for a product in the minds of the target consumers. It differentiates the product from competitors and highlights its unique value proposition.
Example: Positioning a new health drink as the go-to beverage for fitness enthusiasts through targeted marketing campaigns. The brand might emphasize the drink’s natural ingredients, health benefits, and endorsement by fitness influencers.
Customization
Customization involves personalizing marketing messages and products to meet the specific needs of individual consumers. It enhances the relevance and appeal of marketing efforts.
Example: Using data from previous purchases to offer personalized product recommendations to online shoppers. An e-commerce site might send tailored emails featuring products similar to those previously bought by the customer, increasing the likelihood of repeat purchases.
Conclusion
Thank you for joining us on this in-depth exploration of marketing at the Indian Digital Marketing Academy. We hope this blog has provided you with valuable insights and a clearer understanding of the fundamental concepts that drive successful marketing strategies. From the meticulous process of market research to the nuanced understanding of consumer behavior and the critical skill of data analysis and interpretation, we’ve covered essential topics that are pivotal in today’s marketing landscape.
At IDMA, we are committed to empowering our students with the knowledge and skills needed to thrive in the digital marketing arena. We encourage you to apply these insights to your own marketing efforts, experiment with new strategies, and continually seek to understand and meet the needs of your target audience. Remember, marketing is not just a profession; it’s an ongoing journey of learning and adaptation. Stay curious, stay innovative, and most importantly, stay connected with your consumers.
We look forward to continuing this journey with you, sharing more insights, and helping you achieve your marketing goals. Thank you for being a part of the IDMA community, and we can’t wait to see the incredible things you’ll accomplish!


